overview
Private education in Kenya is regulated under the Basic Education Act, 2013. It seeks to promote and regulate free and compulsory basic education and provide for accreditation, registration, governance and management of institutions of basic education.
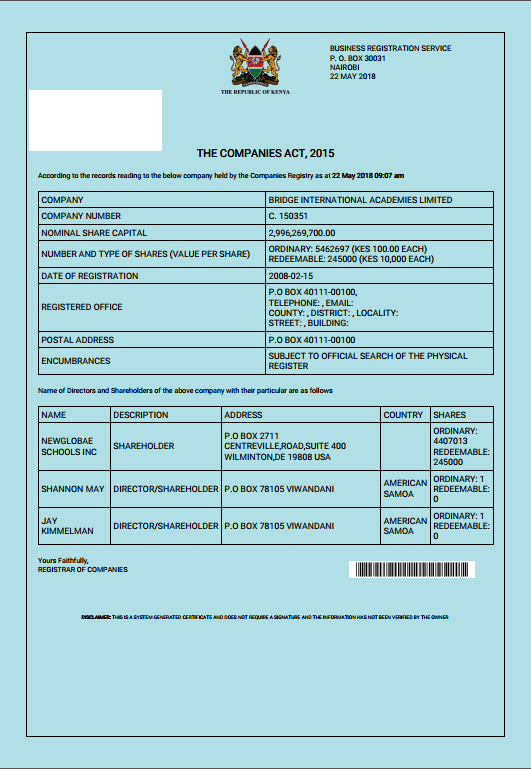
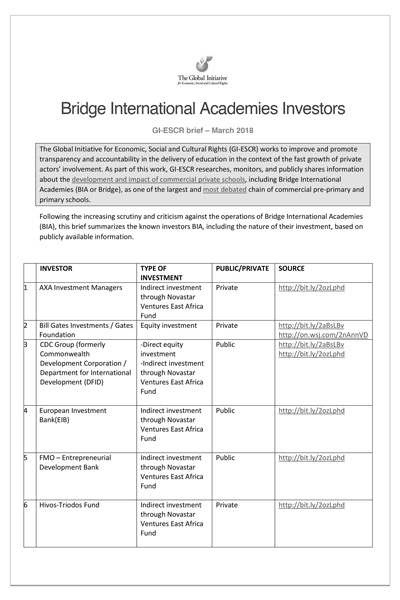
The largest private actor in education in Kenya is Bridge International Academies (BIA). It first opened a school in Mukuru kwa Njenga slum in Kenya in 2009. The company currently operates about 405 schools across Kenya.
Key Updates
The most recent updates on BIA operations in Kenya:
27 October 2019: The World Bank’s accountability body raises ‘substantial concerns’ regarding IFC’S investment in Bridge International Academies
7 June 2019: Work Bank accepts complaint on its investment in BIA
16 April 2018: Kenyan citizens, parents and teachers file complaint against the World Bank for it funding to Bridge International Academics: http://bit.ly/2JLG9kl
23 February 2018: Kenyan court prevents attempts by Bridge International Academies to muzzle critics: http://bit.ly/2CGfZKR
13 November 2017: African Commission raises concerns about lack of regulation of Bridge International Academies: http://bit.ly/2hv8yBZ
+ Read More
Concluding Observations on Kenya by the African Commission on Human and Peoples’ Rights: http://bit.ly/2o1XCLg
Education International and Kenya National Union of Teachers report, ‘Bridge vs. Reality: a study of Bridge International Academies’ for-profit schooling in Kenya’: http://bit.ly/2h1Rml9
19 July 2017: Leaked letter from Ministry of Education finds Bridge in breach of education standards: http://bit.ly/2uaBZfT
17 February 2017: Kenyan court upholds closure of Bridge International Academies in Busia county: http://bit.ly/2lT2vHG
Country Partner
Resources
PRIVATE ACTORS AND THE RIGHT TO EDUCATION CASELAW DATABASE
Key cases on the right to education, particularly in the context of the involvement of private actors.
Resource Database
External documents that support our advocacy efforts for the right to education.
Monitoring Tools
Materials that can support other organisations advocating for the right to education.
Concluding Observations on Private Actors in Education Database
Collection of UN Concluding Observations that related to private actors in education.